Carinacuma umesi, a new genus and species of bodotriid cumacean (Crustacea: Malacostraca: Peracarida) from shallow waters of the Maryland Coastal Bays, Mid-Atlantic region, USA
- Published
- Accepted
- Received
- Academic Editor
- James Reimer
- Subject Areas
- Biodiversity, Marine Biology, Taxonomy, Zoology
- Keywords
- Cumacea, Bodotriidae, Vaunthompsoniinae, Carinacuma gen. nov., Carinacuma umesi sp. nov., North America, Maryland, Mid-Atlantic coast
- Copyright
- © 2021 Morales-Núñez and Chigbu
- Licence
- This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, reproduction and adaptation in any medium and for any purpose provided that it is properly attributed. For attribution, the original author(s), title, publication source (PeerJ) and either DOI or URL of the article must be cited.
- Cite this article
- 2021. Carinacuma umesi, a new genus and species of bodotriid cumacean (Crustacea: Malacostraca: Peracarida) from shallow waters of the Maryland Coastal Bays, Mid-Atlantic region, USA. PeerJ 9:e11740 https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.11740
Abstract
Carinacuma, a new bodotriid cumacean genus, is diagnosed to receive Spilocuma watlingi Omholt & Heard as its type species and C. umesi sp. nov., described from shallow waters (0.8 to 2.8 m) on the Mid-Atlantic coast of North America. Carinacuma gen. nov. has its closest affinities to the North American genera Spilocuma and Mancocuma, but can be distinguished from them and the other genera within the subfamily Vaunthompsoniinae by a combination of characters, including the presence of a dorsal carina or keel on pereonite 3 of the female, morphology of the antenna, absence of pleopods in the male, and the setation and segmentation of the uropods. Carinacuma umesi sp. nov., can be differentiated from its northern Gulf of Mexico cognate, C. watlingi comb. nov. by several characters, including: (1) maxilliped 3 carpus of female with inner margin bearing four to five simple setae, (2) uropod peduncle of female with inner margin bearing one sub-distal micro-serrate seta with single sub-terminal medial setule, (3) male antennule peduncle articles 1–2 sub-equal length, and (4) male antennule accessory flagellum slightly longer than basal article of main flagellum. A key to the five known males lacking pleopods within Vaunthompsoniinae is provided.
Introduction
Members of the order Cumacea are small peracarid crustaceans, usually 1–35 mm in length, which are inhabitants of brackish and marine waters throughout the world (Heard, Roccatagliata & Petrescu, 2007; Gerken, 2018). Nine cumaceans species have been reported from the Chesapeake Bay (Zimmer, 1943; Zimmer, 1980; Wass, 1972). There are no publications, however, on the taxonomy and systematics of cumaceans in the Maryland Coastal Bays (MCBs), though information on the diversity and densities of cumaceans in the bays is available in several State reports (i.e., Llansó, Scott & Kelley, 2002; Llansó, Scott & Kelley, 2003; Llansó, Scott & Kelley, 2004; Llansó, Scott & Kelley, 2005; Llansó, Scott & Kelley, 2006; Llansó & Dew, 2010; Llansó, 2015).
Morales-Núñez & Chigbu (2016) reported a new Maryland distribution record for a bodotriid cumacean tentatively identified as “Spilocuma watlingi Omholt & Heard, 1979”. Upon further examination, however, this species was found to represent an undescribed species closely related to Spilocuma watlingi, which is endemic to the northeast Gulf of Mexico (GoM). The close similarity between S. watlingi and the new species from Maryland, and their distinctive differences with type species of Spilocuma, S. salomani Watling , 1977 necessitate the establishment of a new bodotriid genus within the bodotriid subfamily Vaunthompsoniinae Sars, 1878–1879 sensu Haye (2007).
The descriptions of these new taxa, including information on the abundance, distribution, and habitat of a new East coast species are presented herein.
Materials and Methods
Study area
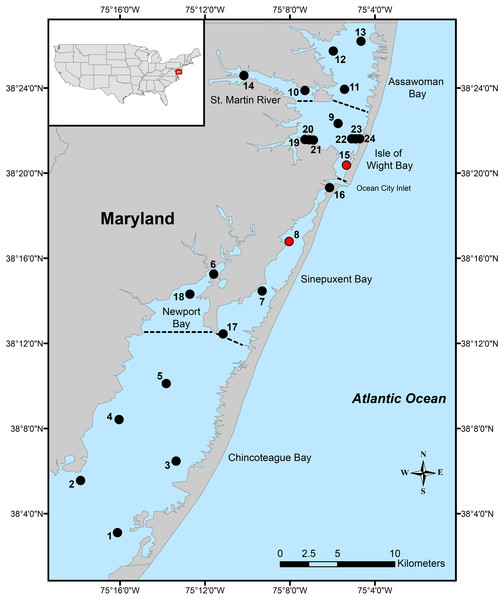
The Maryland Coastal Bays is a barrier-island system located on the eastern part of the Delmarva Peninsula in the eastern USA. The system consists of six principal lagoons/areas: Chincoteague Bay, Newport Bay, Sinepuxent Bay, Isle of Wight Bay, St. Martin River, and Assawoman Bay (Fig. 1).
Figure 1: Local distribution.
Map of Maryland Coastal Bays indicating the 24 stations sampled. Red circles indicate the only stations where Carinacuma umesi gen. et sp. nov was found; dotted lines separate bays/areas.Sample collection and processing
Samples for this study were taken at 24 stations in the MCBs during May, June, August, and November from 2017 to 2019 (Fig. 1); although due to inclement weather conditions, samples were not collected from four stations in the Chincoteague Bay during May 2018. At each station, two sediment grab samples for biological analysis were taken using a 0.026 m2 stainless steel Van Veen grab (total area = 0. 052 m2). In the field, sediment samples for macroinvertebrates were passed through a 0.5 mm sieve screen (Eleftheriou & Mcintyre, 2005). After sieving, all the macroinvertebrates were fixed in 4% formalin with rose Bengal. In the laboratory, fixed macroinvertebrates were hand sorted, preserved in 70% ethanol, counted, and identified to the lowest possible taxonomic level. Additionally, one sample was collected at station-8 during a tryout of the new Van Veen benthic grab in August 2014; but sediment samples and water quality information were not collected.
One sediment sample was also collected for grain size and organic matter content analyses. Samples for grain size distribution and organic matter analyses were dried in a conventional oven at 105 °C and weighed until a constant weight was obtained. Sediment organic matter content was estimated by loss on ignition (LOI) method (Heiri, Lotter & Lemcke, 2001; Eleftheriou & Mcintyre, 2005). Grain size distribution was determined by sieving using the method described by Eleftheriou & Mcintyre (2005) and the United States Geological Survey (USGS) for Coarse Fraction Analysis (Gravel plus Sand). The particle size distribution and sorting of sediment were determined using the GRADISTAT v.9.1 software (Blott & Pye, 2001). Water quality data were collected in situ at each station using a YSI 6600 Multi-Parameter Water Quality Sonde and included water temperature, salinity, dissolved oxygen, and pH, which were all recorded at 0.3 m from the bottom.
Specimens were dissected under an Olympus SXZ-16 stereomicroscope. Appendages were mounted on glass slides in glycerin and observed with an Olympus BX41 compound microscope, and drawings were made with a camera lucida. Drawings were re-drawn with a Wacom Cintiq Pro 13 - Creative Pen and touch display and Adobe Illustrator CC (2020). Figures were prepared with Adobe Illustrator CC (2020) and Photoshop CC (2020). Photographs were taken using an Olympus DP73 digital camera mounted on a stereomicroscope Olympus SXZ16 and all specimens were measured with CellSens dimensions 1.11 software (Olympus). Maps (Figs. 1, 2) were created using ArcGIS 10.4.2 software (University of Maryland Eastern Shore (UMES)).
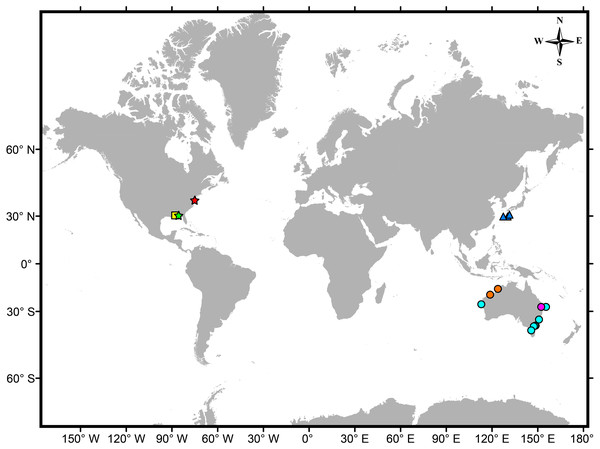
Figure 2: Map showing the worldwide distribution of known genera/species of males lacking pleopods within Vaunthompsoniinae.
Circles –genus Picrocuma: P. crudgingtoni (magenta) (Watling & Gerken, 2020), P. poecilotum (cyan) (Hale, 1936; Tafe & Greenwood, 1996; GBIF Secretariat, 2020a; GBIF Secretariat, 2020b), P. rectangularis (orange) (Mühlenhardt-Siegel, 2003). Triangles –genus Pseudopicrocuma: P. japonicum (blue) (Akiyama, 2012). Star –genus Carinacuma gen. nov.: C. umesi sp. nov. (red) (this study), C. watlingi (light green) (Omholt & Heard, 1979; Modlin, 1992; GBIF Secretariat, 2020a; GBIF Secretariat, 2020b). Square –genus Spilocuma: S. salomani (yellow) (Watling, 1977; Modlin, 1992; GBIF Secretariat, 2020a; GBIF Secretariat, 2020b).The holotype and paratypes were measured and separated into three life-stage categories: (1) non-ovigerous females —without fully developed oöstegites, (2) ovigerous females —with fully developed oöstegites, and (3) male —smaller with strong antenna.
Type material has been deposited in the National Museum of Natural History, Smithsonian Institution, Washington, DC. All measurements were in millimeters. Total body length was measured from the frontal margin of the carapace to the posterior end of the pleon. Setal terminology follows that of Garm & Watling (2013).
Nomenclatural acts
The electronic version of this article in Portable Document Format (PDF) will represent a published work according to the International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN), and hence the new names contained in the electronic version are effectively published under that Code from the electronic edition alone. This published work and the nomenclatural acts it contains have been registered in ZooBank, the online registration system for the ICZN. The ZooBank LSIDs (Life Science Identifiers) can be resolved and the associated information viewed through any standard web browser by appending the LSID to the prefix http://zoobank.org/. The LSID for this publication is: [urn:lsid:zoobank.org:pub:3DF884AE-08A7-4CDD-B1D4-A7675ADC7F92]. The online version of this work is archived and available from the following digital repositories: PeerJ, PubMed Central and CLOCKSS.
Results
Systematics
| Order Cumacea Krøyer, 1846 |
| Family Bodotriidae T. Scott, 1901 |
| Subfamily Vaunthompsoniinae Sars, 1878–1879 |
Type genus. Vaunthompsonia Bate, 1858
Diagnosis. After Haye (2007). Exopods occurring beyond first pair of pereopods. Females generally having three or more antennal articles. Uropod endopod generally bi-articulated.
Genera. Apocuma Jones, 1973; Bathycuma Hansen, 1895; Cumopsis Sars, 1878–1879 (= Heterocuma Miers, 1879); Gaussicuma Zimmer, 1907; Gephyrocuma Hale, 1936; Gigacuma Kurian, 1951; Glyphocuma Hale, 1944; Hypocuma Jones, 1973; Carinacuma gen. nov.; Leptocuma Sars, 1873; Mancocuma Zimmer, 1943; Paravaunthompsonia Mühlenhardt-Siegel, 2008; Picrocuma Hale, 1936; Pomacuma Hale, 1944; Pseudoleptocuma Watling, 1977; Pseudopicrocuma Akiyama, 2012; Pseudosympodomma Kurian, 1954; Scyllarocuma Corbera, 2006; Speleocuma Corbera, 2002; Spilocuma Watling, 1977; Sympodomma Stebbing, 1912; Vaunthompsonia; Zenocuma Hale, 1944.
Remarks. Based on morphological phylogenetics analysis, Haye (2007), considered the subfamily Mancocumatinae Watling, 1977 as a junior synonym of the subfamily Vaunthompsoniinae. Further, Haye stated that the genus Heterocuma was synonymized with Cumopsis due to the strong molecular similarity (e.g., 79% bootstrap support) and lack of morphological differentiation (Haye, Watling & Kornfield, 2004; Haye, 2007). Notwithstanding, Luque & Gerken (2019) recently conducted a new morphological phylogenetic analysis of the family Bodotriidae in which they treated Heterocuma and Cumopsis as distinct genera.
Carinacuma Morales-Núñez gen. nov.
Spilocuma.—Omholt & Heard, 1979 (in part).
Type-species. Carinacuma watlingi (Omholt & Heard, 1979) comb. nov.
Diagnosis. Female. Carapace lacking ridges or denticulations. Pereonite 3 with distinct dorsal keel or carina. Pereonite 5 with ventral keel or carina. Antennule peduncle having three articles; article 1 less than combined length of 2 and 3; peduncle articles 2 and 3 subequal; main flagellum subequal to peduncle article 3, main flagellum article 2 with two aesthetasc. Antenna with four articles. Maxilliped 3 with basis having distal angle not produced. Pereopod 1 without distal brush of setae on propodus and dactylus. Well-developed exopods present on pereopods 1–3; rudimentary on pereopod 4. Uropod: peduncle with inner margin bearing 1–6 simple or serrate setae with or without subterminal setule; endopod article 1 with inner margin having 4–7 bilaterally serrate seta with single sub-terminal medial setule, endopod article 2 with inner distal margin having one bilaterally serrate seta with single sub-terminal medial setule; exopod article 2 with inner distal margin bearing three micro-serrate setae with single sub-terminal medial setule.
Male. Pereonite 3 lacking dorsal keel or carina. Pereonite 5 with or without ventral keel or carina. Antennule with main flagellum tri-articulated. Antenna short not extending past carapace, modified for clasping female, peduncle stout with article-3 sparsely setose (lacking dense cluster of setae); flagella shorter than peduncle with modified “pad-like” setae on articles 10 and 11. Pleopods absent. Uropod: endopod having inner margin of article 1 bearing six bilaterally serrate seta with single sub-terminal medial setule; exopod article 2 having one micro-serrate seta with single sub-terminal setule medial seta on distal inner margin.
Etymology. From the Latin prefix (Carina) = keel, referring to the dorsal keel on the third pereonite of females + Cuma from which the ordinal name derives.
Gender. Feminine.
Species. Carinacuma umesi sp. nov.; C. watlingi (Omholt & Heard, 1979) comb. nov.;
Distribution. Known from shallow (0.5 to 3 m) coastal waters of the northwest Atlantic coastal region of North America (Maryland Coastal Bays, Mid-Atlantic region) and the northeast Gulf of Mexico (GoM), i.e., Alabama, Mississippi, and northwest Florida).
Remarks. Carinacuma gen. nov. appears to be most similar to the now monotypic genus Spilocuma, which is endemic to the northeast Gulf of Mexico, and to Mancocuma Zimmer, 1943, which is endemic to the Atlantic seaboard of North America. The female of Carinacuma is characterized by a dorsal keel or carina on pereonite 3, which immediately distinguishes it from these two genera, as well as, the other taxa within the subfamily Vaunthompsoniinae.
The male of Carinacuma also exhibits similarities to those of Mancocuma and Spilocuma. They all share specialized, short or relatively short prehensile “clasping” antennae, not extending posteriorly past the pereon, with stout peduncle (modified in varying degrees), and flagella curved ventromedially in a pre-copulatory, clasping orientation. The presence in the male of two pairs of reduced pleopods and a longer antenna flagellum with 20 or more articles in the less derived Mancocuma readily separates it from Carinacuma and Spilocuma.
The males of Carinacuma and Spilocuma are similar in having their antenna peduncles slightly longer than the flagella and lacking pleopods. Carinacuma, however, is distinguished from Spilocuma by having a: (1) uropod endopod article-1 with inner margin bearing six bilaterally serrate seta with single sub-terminal medial setule (14 in Spilocuma), (2) uropod endopod article-2 with inner margin having one bilaterally serrate seta with single sub-terminal medial setule (four in Spilocuma), and (3) uropod exopod with article 2 inner margin bearing one micro-serrate seta with single sub-terminal setule medial seta (two in Spilocuma).
As in the males of Carinacuma gen. nov. and Spilocuma, the genera Picrocuma from eastern Australia (Hale, 1936) and Pseudopicrocuma from southern Japan (Akiyama, 2012) lack pleopods. The number of pleopods on the other males within the subfamily Vaunthompsoniinae ranges from two to five pairs. There are two pairs on Mancocuma and Speleocuma; three pairs on Pseudoleptocuma; and five pairs on Apocuma, Bathycuma, Cumopsis (= Heterocuma), Gaussicuma, Gephyrocuma, Gigacuma, Glyphocuma, Hypocuma, Leptocuma, Paravaunthompsonia, Pomacuma, Pseudoleptocuma, Pseudosympodomma, Sympodomma, Vaunthompsonia. Males are unknown for the genera Scyllarocuma and Zenocuma.
At present the species representing Carinacuma and Spilocuma are known only from shallow-temperate and warm-temperate waters of the Atlantic and Gulf coasts of North America (Fig. 2). The other two genera are Picrocuma from western and eastern coasts of Australia (Fig. 2, Table 1) and Pseudopicrocuma from relatively deep-water (566–1679 m) in the northwestern Pacific Ocean (Fig. 2, Table 1). Based on other distinct morphological differences in their males, it is probable that the Vaunthompsoniinae genera from the Atlantic (Carinacuma, Spilocuma) and Pacific (Picrocuma, Pseudopicrocuma) are phylogenetically distant. In this case the mutual loss of pleopods would be due to homoplasy. These four genera and their species can be further distinguished using a dichotomous key presented herein.
| Genus | Geographical area | Depth range (m) |
|---|---|---|
| Apocuma | Atlantic Ocean New south Wales, Victoria, and Tasmania |
587–2003 119–1500 |
| Bathycuma | North Atlantic, Indian, and Pacific Oceans, Mediterranean Sea and off the coasts of South Africa | 5000 |
| Cumopsis (= Heterocuma) | East Atlantic and west Pacific Oceans and Mediterranean Sea | 0–200 |
| Gaussicuma | Southern Ocean Northwest Pacific Ocean |
3400–4600 42–105 |
| Gephyrocuma | Australian coast | 0–75 |
| Gigacuma | Indo-west Pacific | 7–27 |
| Glyphocuma | Southern Australian coast | 0–100 |
| Hypocuma | South Africa North Atlantic |
400 1000–5000 |
| Carinacumagen. nov. | Northwest Atlantic Ocean (Gulf of Mexico and Mid-Atlantic region) | 0.5–3 |
| Leptocuma | Northeast Pacific Ocean Australian and South American |
10 0–190 |
| Mancocuma | Northwest Atlantic Ocean | 0–18 |
| Paravaunthompsonia | Red Sea | 1446 |
| Picrocuma | Southeast Indian Ocean and southwest Pacific Ocean (Australia) | 1–4 |
| Pomacuma | Australia and New Zealand | 0–75 |
| Pseudoleptocuma | Northwest Atlantic Ocean | 15–24 |
| Pseudopicrocuma | Northwest Pacific Ocean (Southern Japan) | 566–1679 |
| Pseudosympodomma | West Pacific Ocean (Tanzania) and Indo-west Pacific South Africa |
0–4 85–370 |
| Scyllarocumaa | Southwest Pacific Ocean (New Caledonia, Australia) | 650 |
| Speleocuma | Northeast Atlantic Ocean (Tenerife, Canary Islands) | 7 (cave complex) |
| Spilocuma | Northwest Atlantic Ocean Gulf of Mexico (Florida) | 3 |
| Sympodomma | West Indian Ocean, Indo-west and west Pacific, Australian coast, and South Pacific | 115–1158 |
| Vaunthompsonia | Mediterranean and red Seas, Indo-west and North Pacific, northwest tropical Atlantic (Caribbean Sea), Indian and Southern Oceans | 0–280 |
| Zenocumaa | Southwest Pacific Ocean (Australia) | 30–75 |
Notes:
Carinacuma watlingi (Omholt & Heard, 1979) comb. nov.
Spilocuma watlingi Omholt & Heard, 1979: 184–194, figs. 1–5.—Băcescu, 1988: 100.—Hopkins, Valentine & Lutz, 1989: 113, 115, 43e-f (key).—Rakocinski et al., 1991: 693.—Modlin, 1992: 83–90, fig 2., Table 1.— Rakocinski et al., 1996: 350 (Appendix 1).— Camp, 1998: 138 (List). —Heard, Roccatagliata & Petrescu, 2007: 35 (key), 105. —Heard & Roccatagliata, 2009: 1009 (check list).
Type material. United States National Museum. Not seen.
Material examined. Non-ovigerous ♂ (GCRL 05745), TBL 2.2 mm, station D4, Gulf of Mexico, Florida, USA, depth 1.5 m, sand, collector Sara E. LeCroy, 04 October 1989.—Adult ♂ (GCRL 05746), TBL 1.3 mm, station C6, (30° 18.37′N–87° 21.67′W), Gulf of Mexico, Florida, USA, depth 1.8 m, sand, collector Cathy Wooten, 04 December 1991.
Diagnosis. Modified from Omholt & Heard (1979). Female. Antenna second article without setae or spines. Maxilliped 3 with carpus having 7–8 internal spines; propodus with four internal spines. Uropod: peduncle with inner margin bearing 3–6 sub-distal micro-serrate seta with single sub-terminal medial setule; endopod article 1 with inner margin having 4–6 bilaterally serrate seta with single sub-terminal medial setule.
Male. Antennule accessory flagellum shorter than basal article of main flagellum.
Depth. 1–1.8 m.
Type locality: Mobile Bay, southeast end of Dauphin Island, Alabama, 30°14′21″N, 88°04′42″W.
Distribution. Gulf of Mexico (Alabama, Mississippi, northwest Florida).
Remarks. Carinacuma watlingi comb. nov., which is endemic to the northern GoM, is clearly congeneric and a cognate or sister species of the new species described herein from Maryland Coastal Bays.
Carinacuma umesi Morales-Núñez sp. nov.
Synonym: Spilocuma watlingi Morales-Núñez & Chigbu, 2016
Material examined. Holotype—Ovigerous ♂ (USNM 1658948), TBL 2.5 mm, station-15 (38°20.398′N–75°05.290′W), Isle of Wight Bay, Maryland, USA, depth 2.6 m, sand substrata, temperature 24.8 °C, salinity 32.8 PSU, DO 5.8 (mg/L), pH 7.8, collectors Andrés G. Morales-Núñez and Kayle Krieg, 10 August 2018.
Paratypes—Ovigerous female ♂ (dissected) (USNM 1658949), TBL 2.3 mm, station-15 (38°20.398′N–75°05.290′W), Isle of Wight Bay, Maryland, USA, depth 2.8 m, sand substrata, temperature 25.5 °C, salinity 30.9 PSU, DO 7.1 (mg/L), pH 7.6, collected by Andrés G. Morales-Núñez, 17 August 2017.—Ovigerous female ♂ (USNM 1658950), TBL 2.5 mm, station-8 (38°16.825′N–75°08.032′W), Sinepuxent Bay, Maryland, USA, depth 0.8 m, sand substrata, collectors Andrés G. Morales-Núñez and Alexis Jackson, 29 August 2014.—Non-ovigerous ♂ (USNM 1658951), TBL 2.3 mm, same collection data as holotype.—Adult ♂ (USNM 1658952), TBL 1.5 mm, same collection data as holotype.
Diagnosis. Female. Antenna article 2 with sub- distal robust seta. Maxilliped 3 with carpus having four simple setae on inner margin. Uropod peduncle with inner margin bearing one sub-distal micro-serrate seta with single sub-terminal medial setule. Uropod endopod article 1 inner margin with 6–7 bilaterally serrate seta with single sub-terminal medial setule.
Male. Antennule having accessory flagellum slightly longer than basal article of main flagellum.
Etymology. Named in honor of the University of Maryland Eastern Shore (UMES); the name is an acronym for UMES.
Type locality. Isle of Wight Bay, Station-15 (38°20.398′N–75°05.290′W), Maryland Coastal Bays, United States of America.
Distribution. Coastal shallow waters of Maryland Coastal Bays, Mid-Atlantic region –USA; Isle of Wight Bay, Station-15 (38°20.398′N–75°05.290′W) and Sinepuxent Bay Station-8 (38°16.825′N–75°08.032′W), at depths ranging from 0.8 to 2.8 m.
Description. Based on ovigerous female (USNM 1658949). Carrying nine eggs.
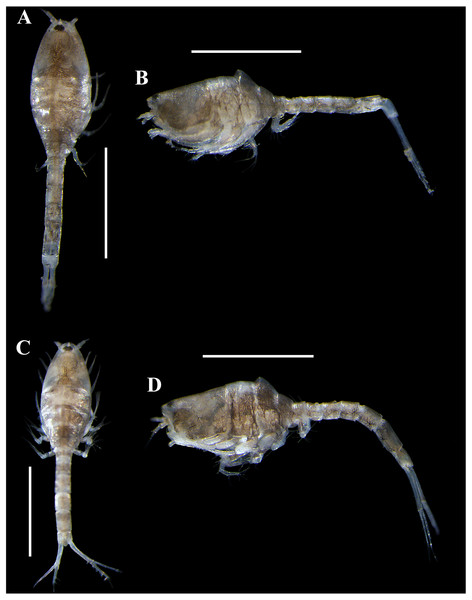
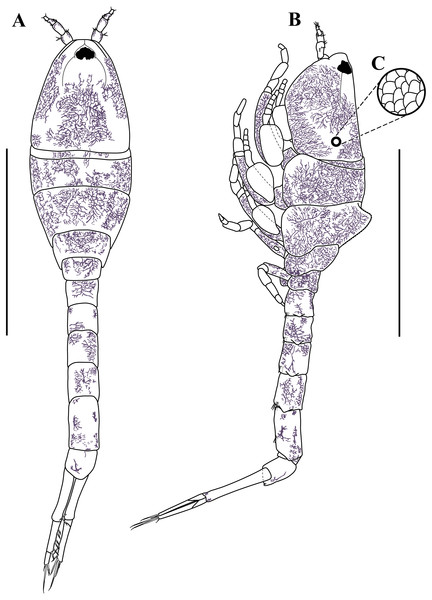
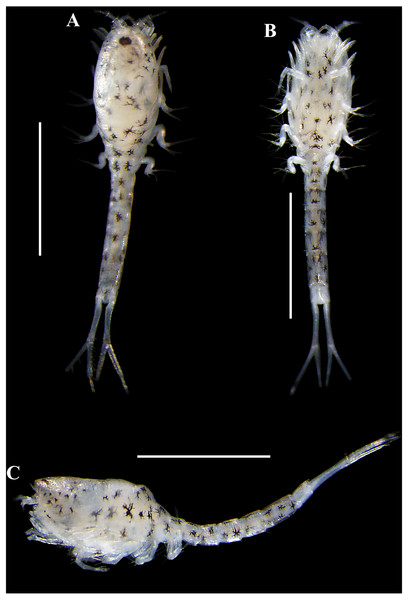
Body (Figs. 3A–3C, 9A–9B). Length 2.3 mm, covered with purplish/brownish chromatophores dotted, integument covered by scales (Fig. 3C).
Carapace (Figs. 3A–3B, 9A–9B). About 25% of TBL, shorter than pereon, longer than wide; smooth, no ridges present; margins without any denticulation; laterally compressed anteriorly, not oviform; antennal notch shallow; pseudorostral lappets extend beyond frontal lobe and meet in mid-line.
Pereon (Figs. 3A–3B, 9A–9B). About 30% of TBL, shorter than pleon; all five segments visible in dorsal view (Fig. 3A); first pereonite visible only above lateral mid-line (Fig. 3B); second pereonite wide, and overriding pereonite 1 and carapace (Fig. 11B); third pereonite with distinct dorsal keel and overriding four pereonite (Fig. 3B); four pereonite overriding fifth pereonite; fifth pereonite with distinct ventral keel (Fig. 3B).
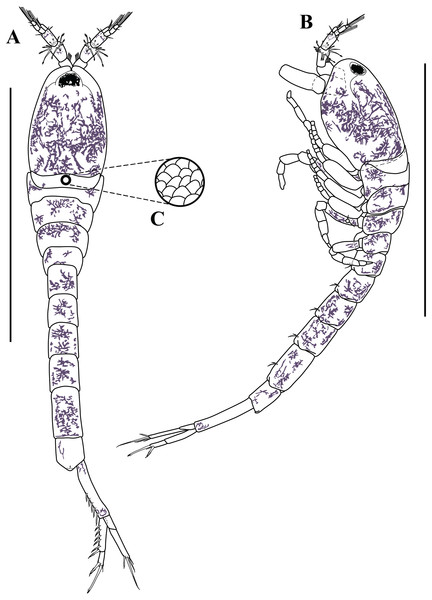
Figure 3: Habitus illustration (ovigerous female).
Carinacuma umesi gen et sp. nov., Paratype ovigerous female: (A) dorsal view; (B) lateral view; (C) enlargement of the body scales. Scale bars = 1.0 mm for A–B.Pleon (Figs. 3A–3B, 8E, 9A–9B). About 45% of TBL, shorter than carapace and pereon together; pleonite 1 shortest; pleonite 5 about 1.9 times as long as wide, longest; pleonites 1–5 with four (two at each side) ventral setae; pleonite 6 asetose; pleonite 6 slightly longer than wide (Fig. 8E), shorter than uropod peduncle (Fig. 3A–3B, Fig. 8E), slightly extended past insertion of uropods (Fig. 8E). Pleopods absent.
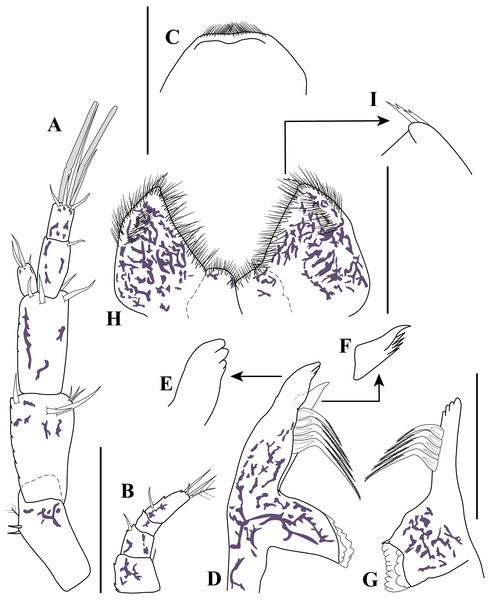
Figure 4: Antennule, antenna, and mouth parts illustrations.
Carinacuma umesi gen. et sp. nov., Paratype ovigerous female: (A) antennule; (B) antenna; (C) labrum; (D) left mandible; (E) enlargement of left incisor; (F) enlargement of lacinia mobilis; (G) right mandible; (H) labium; (I) enlargement of labium tip. Scale bars = 0.1 mm for A–D, G, H.Figure 5: Mouth parts illustrations.
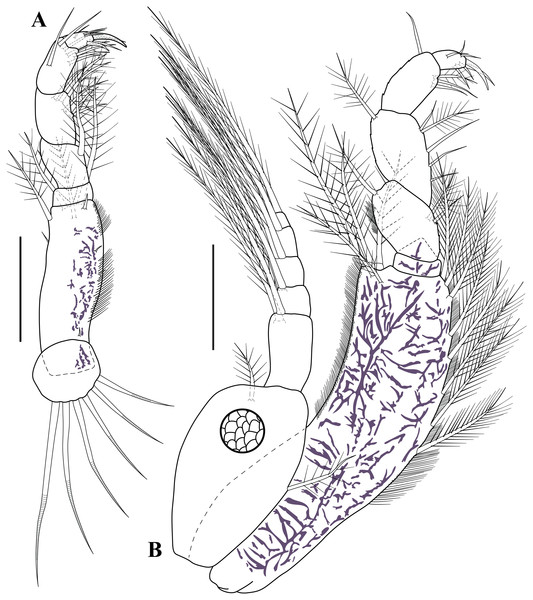
Carinacuma umesi gen. et sp. nov., Paratype ovigerous female: (A) maxillule; (B) maxilla; (C) enlargement of pappose seta; (D) enlargement of microserrate seta; (E) maxilliped 1 (basis and endite); (F) enlargement of coupling hooks; (G) maxilliped 1 (ischium to dactylus); (H) enlargement of thick medially-setose seta. Scale bars = 0.1 mm for A–B, E, G.Antennule (Fig. 4A). Peduncle with three articles; article 1 shortest with two sub-distal robust setae and one broom seta; article 2 twice as long as wide, distally with six simple setae (three small and three robust), article 3 sub-equal to article 2 length with four robust setae distally. Main flagellum bi-articulated; article 1 twice as long as wide with one distal simple seta, article 2 about 1.6 times as long as wide, distally with three robust setae, two simple setae of unequal lengths and two aesthetascs. Accessory flagellum uniarticulated; half-length basal article of main flagellum, distally with three robust setae of varying lengths.
Figure 6: Maxillipeds illustrations.
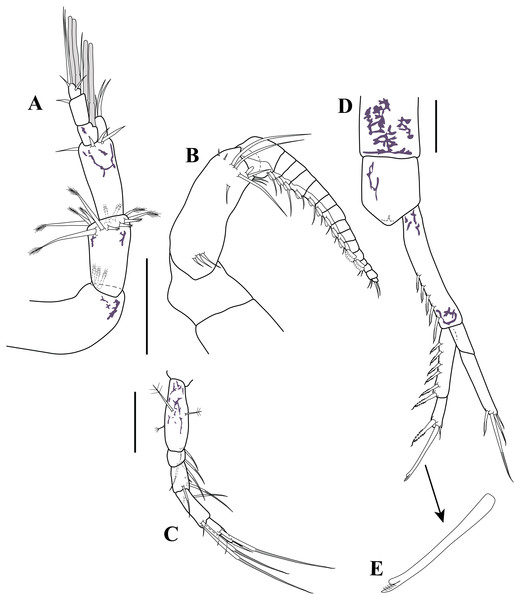
Carinacuma umesi gen. et sp. nov., Paratype ovigerous female: (A) maxilliped 2; (B) maxilliped 3. Scale bars = 0.1 mm.Figure 7: Pereopods and uropod.
Carinacuma umesi gen. et sp. nov., Paratype ovigerous female: (A) pereopod 1; (B) pereopod 2; (C) enlargement of semi-annulate seta; (D) enlargement of strong serrated seta with single sub-terminal medial setule. Scale bars = 0.1 mm for A–B.Antenna (Fig. 4B). Small, with four articles; article 1 wider than long with distal simple seta; article 2 sub-quadrate with sub-distal robust seta; article 3 wider than long, shortest, asetose; article 4 2.4 times longer than width, with sub-proximal robust seta, distally with one robust seta, two simple setae, and one broom seta.
Labrum (Fig. 4C). Distally setulate.
Mandibles (Figs. 4D–4G). Naviculoid form (not illustrated). Left and right mandible incisor with four denticles (Figs. 4D–4E, 4G); lacinia mobilis broad with five uneven teeth only present on left mandible (Fig. 4F); left and right setiferous lobe with five microserrate setae medially of different lengths (Figs. 4D, 4G). Molar process of left and right mandible similar, with grinding surface with well-developed micro-denticles (Figs. 4D, 4G).
Figure 8: Pereopods and uropod.
Carinacuma umesi gen. et sp. nov., Paratype ovigerous female: (A) pereopod 3; (B) enlargement of annulate seta; (C) pereopod 4; (D) pereopod 5; (E) Uropod; (F) micro-serrate seta with single sub-terminal setule medial seta; (G) serrate seta with single sub-terminal setule medial seta; (H) micro-serrate seta. Scale bars = 0.1 mm for A, C–E.Figure 9: Pictures of habitus of Carinacuma umesi gen. et sp. nov. from Maryland Coastal Bays.
Ovigerous female (dissected), paratype, TBL 2.3 mm: (A) dorsal view; (B) lateral view. Ovigerous venus , holotype, (USNM 1658948), TBL 2.5 mm: (C) dorsal view; (D) lateral view. Scale bars = 1.0 mm. Photos by A.G. Morales-Núñez.Labium (Figs. 4H–4G). Inner margin setulose (Fig. 4H), mid-outer distal margin setulose (Fig. 4H), with two forked distal setae (Figs. 4H–4I).
Maxillule (Fig. 5A). With two endites; inner endite distal margin with five (two curved) simple setae and one trifurcate seta; outer endite distal margin with 12 simple setae; palp with two distal setae.
Maxilla (Figs. 5B–5D). With three endites; broad endite distal margin with five pappose (Fig. 5C) and five simple setae (Fig. 5B), and inner row of eight basally-swollen setae (Fig. 5B); inner narrow endite distal margin with three microserrate setae (Fig. 5D); distal narrow endite having distal margin with five microserrate and three simple setae, both narrow endites not extending past distal margin of broad endite (Fig. 5B).
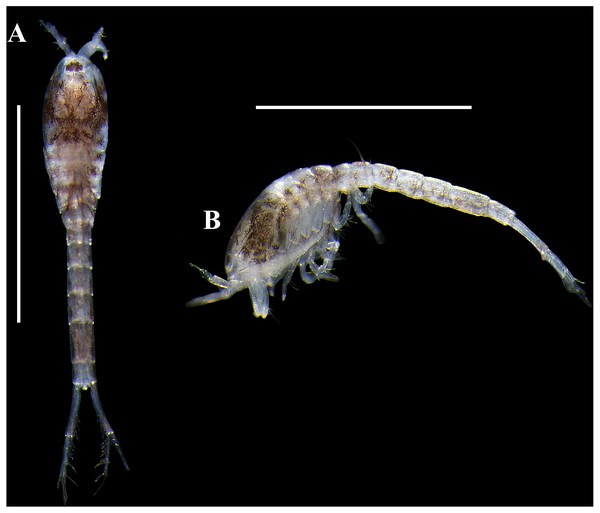
Figure 10: Pictures of habitus of Carinacuma umesi gen. et sp. nov. from Maryland Coastal Bays.
Non-ovigerous female , paratype (USNM 1658951), TBL 2.3 mm: (A) dorsal view; (B) ventral view; (C) lateral view. Scale bars = 1.0 mm. Photos by A.G. Morales-Núñez.Figure 11: Habitus illustration (male).
Carinacuma umesi gen et sp. nov., Paratype male: (A) dorsal view; (B) lateral view; (C) enlargement of the body scales. Scale bars = 1.0 mm for A–B.Maxilliped 1 (Fig. 5E–5H). Basis greater than combined lengths of remaining articles (Fig. 5E). Endite inner margin with row of five pappose setae (Fig. 5E), three subdistal simple setae (Fig. 5E), and two coupling hooks (Fig. 5F), distal margin with five pappose setae. Ischium absent. Merus wider than long, shortest, with four pappose setae distally. Carpus 2.4 times merus length, longest, inner margin with 11 simple setae and five thick medially-setose setae (Fig. 5H), sub-distal outer margin with plumose seta. Propodus 2.2 times as long as wide, sub-distal inner margin with four (two simple and two pappose) setae. Dactylus 2.8 times as long as wide, with four (two sub-distal and two distal) simple setae of unequal lengths.
Maxilliped 2 (Fig. 6A). Coxa with six annulate setae. Basis 2.9 times as long as wide, shorter than combined lengths of other articles; inner margin finely setulose, with two small simple setae; sub-distal margin with one plumose seta, and distal margin with two plumose setae and simple seta; sub-distal outer margin with one small simple seta and one plumose seta. Ischium wider than long, shortest, asetose. Merus slightly shorter than carpus, with sub-distal inner plumose seta. Carpus 1.5 times as long as wide, inner margin with oblique row of four plumose setae and two (i.e., one mid and one sub-distal) plumose setae. Propodus 1.8 times as long as wide, twice dactylus length, inner margin with oblique row of four simple setae and two (one simple one plumose) sub-distal setae; mid-outer margin with one simple seta. Dactylus with inner margin bearing two sub-distal setae; distal margin with two (i.e., one simple and one strongly curved) setae; outer margin with simple setae mid-laterally and two simple setae sub-distolaterally.
Maxilliped 3 (Fig. 6B). Basis 3.6 times as long as wide, greater than combined lengths of remaining articles, distal angle not produced; inner margin finely setulose, with eight plumose setae; outer margin finely setulose, with five plumose distally. Ischium wider than long, shorter than merus, asetose. Merus subequal to carpus; sub-distal inner margin with two plumose setae; mid-outer margin finely setulose with sub-distal plumose seta. Carpus shorter than propodus; inner margin with four simple setae of unequal lengths and one plumose seta; sub-distal outer margin with plumose seta. Propodus 1.6 times as long as wide; inner margin with three (one plumose and two simple) sub-distal setae; sub-distal outer margin with simple seta. Dactylus 1.6 times as long as wide; inner margin with two sub-distal setae; distal margin with two (i.e., one simple and one strongly curved) setae; outer margin with mid-laterally simple setae and two sub-distal laterally simple setae. Exopod 0.5 basis length; basal article unarmed; mid-inner margin with plumose seta; sub-distal margin with plumose seta; flagellum with five articles, each article bearing two plumose setae (not all illustrated).
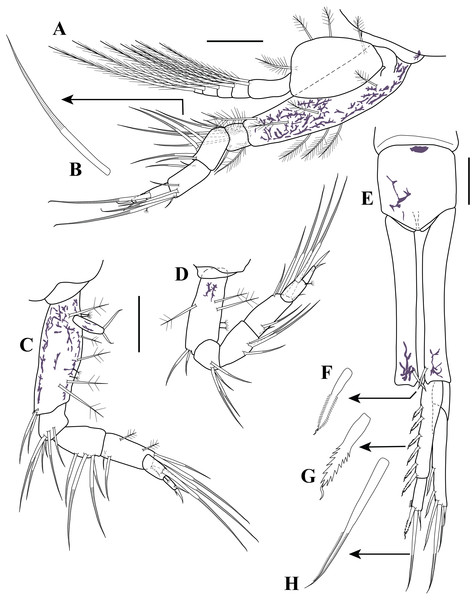
Pereopod 1 (Fig. 7A). Basis 3.0 times as long as wide, greater than combined lengths of remaining articles; inner margin with two sub-proximal broom setae and ∼13 plumose setae; mid-outer margin with five plumose setae; outer margin with plumose seta distally. Ischium shortest; inner margin with sub-distal simple seta. Merus 1.8 times as long as wide, shorter than carpus; inner margin with sub-distal simple seta. Carpus 2.2 times as long as wide, longer than propodus; inner margin with two (one mid and one sub-distal) simple setae; outer margin with one plumose seta distally. Propodus 2.1 times as long as wide; inner margin with sub-distal simple seta; outer margin with sub-distal simple seta. Dactylus 2.6 times as long as wide, shorter than propodus; distal margin with five simple setae; mid-outer margin with simple seta. Exopod 0.6 basis length; basal article unarmed; mid-inner margin with plumose seta; sub-distal margin with plumose seta; sub-distal outer margin with plumose seta; flagellum with seven articles, each article bearing two plumose setae (not all illustrated).
Pereopod 2 (Figs. 7B–7D). Endopod shorter than first pereopod. Basis 2.7 times as long as wide, slightly shorter than combined lengths of remaining articles; inner margin with ten plumose setae; mid-outer margin with five semi-annulate setae (Fig. 7C); outer margin with two (one sub-proximal and one distal) plumose setae. Ischium wider than long, shorter than merus; inner margin with sub-distal simple seta. Merus 1.3 times as long as wide: inner margin with sub-distal strongly serrated seta with single sub-terminal medial setule (Fig. 7D); outer margin with sub-distal semi-annulate seta. Carpus 1.5 times as long as wide; inner margin with two (i.e., one semi-annulate and one sub-distal strongly serrated with single sub-terminal medial setule) setae; outer margin with sub-distal semi-annulate seta. Propodus twice as long as wide; outer margin with three sub-distal semi-annulate setae of different lengths. Dactylus 3.4 times as long as wide, longer than propodus; inner margin with three sub-distal semi-annulate setae of different lengths; distal margin with four simple setae of unequal lengths. Exopod 0.8 basis length; basal article unarmed; inner margin with mid-plumose seta; sub-distal margin with plumose seta; mid-outer margin with three plumose setae; flagellum with six articles, each article bearing two plumose setae (not all of them illustrated).
Pereopod 3 (Figs. 8A–8B). Endopod shorter than first pereopod. Basis 3.4 times as long as wide, greater than combined lengths of remaining articles; inner margin with three plumose setae; mid-outer margin with three plumose setae; distal margin with three plumose setae; outer margin with sub-distal plumose setae. Ischium wider than long, shorter than merus; sub-distal margin with six annulate setae of varying lengths (Fig. 8B). Merus 1.7 times as long as wide; inner distal margin with four annulate setae. Carpus 2.2 times as long as wide; outer margin with sub-distal oblique row of five annulate setae of unequal lengths. Propodus 2.2 times as long as wide; sub-distal margin with one annulate seta; outer margin with distal broom seta. Dactylus twice as long as wide, shorter than propodus; sub-distal margin with simple seta; distal margin with simple seta. Exopod about 0.7 basis length; basal article unarmed; sub-distal margin with plumose seta; mid-outer margin with two plumose setae; flagellum with five articles, each article bearing two plumose setae (not all illustrated).
Pereopod 4 (Fig. 8C). Shorter than first three pereopods. Basis 2.7 times as long as wide, shorter than combined lengths of remaining articles; inner distal margin with two annulate setae and one small simple seta; mid-outer margin with two (i.e., one sub-proximal and one sub-distal) plumose setae; outer margin with four broom setae and three plumose setae. Ischium wider than long, shorter than merus; sub-distal margin with six annulate setae of varying lengths. Merus 1.4 times as long as wide; inner distal margin with four annulate setae. Carpus 2.3 times as long as wide; inner margin with three (two sub-proximal and one distal) annulate setae of unequal lengths; outer margin with two (one sub-proximal and one sub-distal) plumose setae and sub-distal oblique row of five annulate setae of different lengths. Propodus 1.8 times as long as wide; distal margin with one broom seta; sub-distal outer margin with annulate seta. Dactylus 2.8 times as long as wide, shorter than propodus; distal margin with two (i.e., one small simple and one strongly curved) setae; sub-distal outer margin with simple seta. Rudimentary exopod, 3.5 times as long as wide; distal margin with two setae.
Pereopod 5 (Fig. 8D). Basis 2.4 times as long as wide, shorter than combined lengths of remaining articles; inner margin with mid-plumose seta and two sub-distal annulate setae; mid-outer margin with two plumose setae; outer margin with two sub-distal broom seta. Ischium wider than long, shorter than merus; sub-distal margin with four annulate setae of varying lengths. Merus 1.6 times as long as wide; mid-inner margin with three annulate setae of unequal lengths. Carpus 1.9 times as long as wide; inner margin with three (two sub-proximal and one distal) annulate setae of unequal lengths; outer margin with sub-distal oblique row of four annulate setae of varying lengths. Propodus twice as long as wide; distal margin with one broom seta; sub-distal outer margin with annulate seta. Dactylus twice as long as wide, shorter than propodus; distal margin with one strongly curved seta; sub-distal outer margin with simple seta.
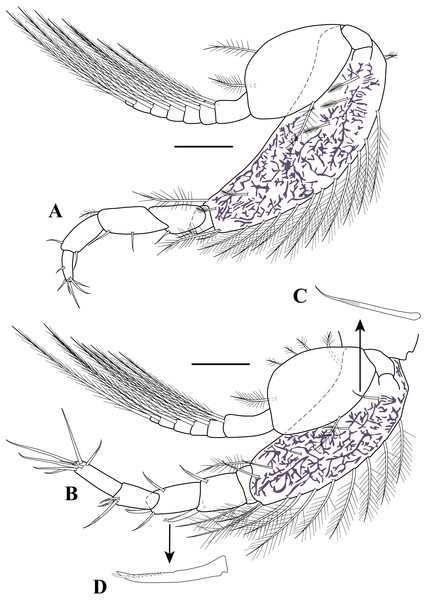
Uropod (Figs. 8E–8H). Peduncle 8.0 times as long as wide, longer than pleonite 6, longer than rami (excluding setae); inner margin with one sub-distal micro-serrate seta with single sub-terminal medial setule (Fig. 8F). Endopod biarticulated: article 1 7.0 times as long as wide, inner margin with six bilaterally serrate setae with single sub-terminal medial setule (Fig. 8G); article 2 3.1 times as long as wide; sub-distal inner margin finely setulose; distal margin with three setae (one bilaterally serrate seta with single sub-terminal medial setule and two micro-serrate setae (Fig. 8H)). Exopod bi-articulated: article 1 1.6 times as long as wide, asetose; article 2 8.0 times as long as wide, inner distal margin with three micro-serrate setae with single sub-terminal medial setule, distal margin with three micro-serrate setae of varying lengths.
Non-ovigerous female (without fully developed oostegites). Similar to ovigerous female except for having an underdeveloped dorsal keel on third pereonite.
Body (Figs. 10A–10B ). Length 2.3 mm.
Carapace (Figs. 10A–10B). About 25% of TBL.
Pereon (Figs. 10A–10B). About 30% of TBL. Third pereonite with an underdeveloped dorsal keel (Fig. 10C).
Pleon (Figs. 10A–10B). About 50% of TBL.
Male. Overall similar to adult females, except having: (1) smaller, more elongate, narrower body, (2) longer and robust antenna, (3) no dorsal keel, and (4) uropod peduncle with several setae. The only male obtained was grasping an ovigerous female when collected.
Body (Figs. 11A–11C, 13A–13B). Small, TBL 1.5 mm, covered with purplish/brownish chromatophores dotted, integument covered by scales (Fig. 11C).
Carapace (Figs. 11A–11B, 13A–13B). About 30% of TBL, longer than pereon, longer than wide; smooth, no ridges present; margins without any denticulation, laterally compressed anteriorly, not oviform.
Pereon (Figs. 11A–11B, 13A–13B). About 20% of TBL, shorter than pleon; all five segments visible in dorsal view (Fig. 11A); first pereonite visible only above lateral mid-line (Fig. 11B); second pereonite wide, and overriding pereonite 1 and carapace (Fig. 11B); third pereonite without dorsal keel (Fig. 11B); fifth pereonite with distinct ventral keel or carina (Fig. 3B).
Pleon (Figs. 11A–11B, 12D, 13A–13B). About 50% of TBL, sub-equal to carapace and pereon together; pleonite 1 shortest; pleonite 5 about 1.8 times as long as wide, longest; pleonites 1–5 with four (two on each side) ventral setae; pleonite 6 asetose, longer than wide (Figs. 11A, 12D), shorter than uropod peduncle (Figs. 11A–11B, 12D), slightly extended past the insertion of the uropods (Fig. 8E). Pleopods absent.
Figure 12: Male illustrations (parts).
Carinacuma umesi gen. et sp. nov., Paratype male: (A) antennule; (B) antenna; (C) pereopod 5; (D) Uropod; (E) enlargement of bifid tip seta. Scale bars = 0.1 mm for A–D.Antennule (Fig. 12A). Peduncle with three articles; article 1 longest with three robust setae; article 2 twice as long as wide, with a crown of 12 robust setae sub-distally, article 3 sub-equal to article 2 length with four robust setae of unequal lengths distally. Main flagellum tri-articulated; article 1 about 1.2 times as long as wide with two aesthetascs; article 2 longest, 1.8 times as long as wide, distally with one robust seta and one simple seta; article 3 shortest, with two (one sub-distal and one distal) small robust setae, with two simple setae of unequal lengths, and two aesthetascs. Accessory flagellum uni-articulated; slightly longer than basal article of main flagellum, distally with three robust setae of varying lengths.
Antenna (Fig. 12B). Robust, geniculate, clasping form; peduncle with three articles; article 1–2 wider than long, asetose; article 3 longest, 2.8 times as long as wide, longer than article 1–2 combined, with three setae sub-proximally, nine setae of varying lengths sub-distally, and one flattened granulated adhesive pad on distal margin. Flagellum with 15 articles; articles 1–11 each with two flattened granulated adhesive pads, being larger on the articles 10–11 and passing next article; article 12–15 lacking pads; articles 1 −11 with one seta distally; articles 12 and 14 with two setae distally; article 13 asetose; article 15 terminating in two setae.
Pereopod 5 (Fig. 12C). Basis 3.1 times as long as wide, shorter than combined lengths of remaining articles; inner margin with mid-plumose seta and two sub-distal annulate setae; mid-outer margin with one plumose seta; outer margin with one broom seta. Ischium wider than long, shorter than merus; sub-distal margin with three annulate setae of varying lengths. Merus 1.7 times as long as wide; mid-inner margin with three annulate setae of unequal lengths. Carpus 2.5 times as long as wide; sub-proximally inner margin with one annulate seta; sub-proximally mid-outer margin with one small simple seta; distal outer margin with one seta and two annulate setae of varying lengths. Propodus twice as long as wide; distal inner margin with one seta; sub-distal inner margin with annulate seta. Dactylus twice as long as wide, shorter than propodus; distal margin with one strongly curved seta; sub-distal outer margin with simple seta.
Uropod (Figs. 12D–12E). Peduncle 5.6 times as long as wide, longer than pleonite 6, longer than rami (excluding setae); inner margin with five sub-distal micro-serrate setae with single sub-terminal medial setule (Fig. 12D). Endopod bi-articulated: article 1 about 4.9 times as long as wide, inner margin with six bilaterally serrate setae with single sub-terminal medial setule (Fig. 12D); article 2 about three times as long as wide; distal margin with three (one bilaterally serrate seta with single sub-terminal medial setule, one long distal bifid tip (one tip rounded and one tip serrate, Fig. 12E), and one small micro-serrate) setae (Fig. 12D). Exopod bi-articulated: article 1 twice as long as wide, asetose; article 2 5.3 times as long as wide, inner distal margin with one micro-serrate seta with single sub-terminal medial setule, distal margin with three micro-serrate setae of varying lengths.
Intraspecific variation. Although only five specimens of Carinacuma umesi sp. nov. were available for the study, they exhibited some degree of variations among the individuals examined (Table 2) including: (1) the number of setae on the inner margin of the carpus of maxilliped 3 varied from four to five (holotype, USNM 1658948), (2) the number of setae on the sub-distal inner margin of the carpus and propodus varied from one to two (holotype, USNM 1658948), respectively, and (3) uropod peduncle with 6–7 (holotype, USNM 1658948) serrate setae with single sub-distal micro-serrate seta with single sub-terminal medial setule on inner margin.
Size distribution. Body sizes of Carinacuma umesi are presented in Table 2. Non-ovigerous female TBL 2.3 mm (Fig. 10). Ovigerous females ranged in size from 2.3 mm to 2.5 mm (n = 3) (Fig. 9). Male TBL 1.5 mm (Fig. 13).
Figure 13: Pictures of habitus of Carinacuma umesi gen. et sp. nov. from Maryland Coastal Bays.
Adult male, paratype, (USNM 1658952), TBL 1.5 mm: (A) dorsal view; B, lateral view. Scale bars = 1.0 mm. Photos by A.G. Morales-Núñez.Coloration. Habitus of non-ovigerous female presented a whitish coloration with black chromatophores dotted (Fig. 10). Meanwhile, habitus of ovigerous females and male presented a darker coloration with purplish/brownish chromatophores dotted (intensity can vary) (Figs. 9 and 13); color in male is more intense (Fig. 13). Following preservation in 70% ethanol for almost six years, the ovigerous female collected in 2014 retained the coloration pattern, as did the other specimens. The exopods in all the specimens examined lack coloration.
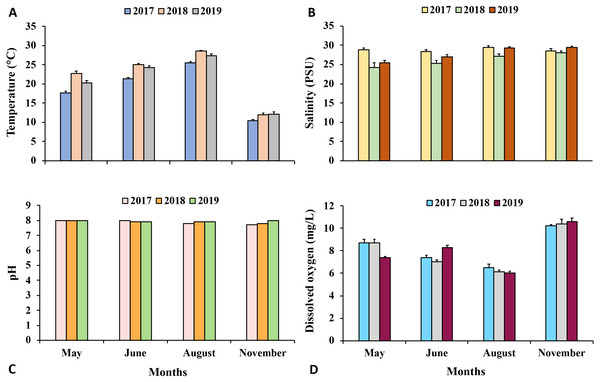
Ecological notes. A total of five individuals of Carinacuma umesi were found in the MCBs. Specimens of C. umesi were only found at two of the 24 stations along the bays (Fig. 1) and were collected from sandy bottoms with, very well sorted, fine sand substrata having low organic content 0.4% ±0.1. Water temperature varied from 24.8–25.5 °C, salinity ranged from 30.9–32.8 PSU, pH varied from 7.6–7.8, and DO ranged from 5.8–7.1 (mg/L). The physicochemical parameters of the surrounding waters where C. umesi was collected are presented in Fig. 14.
Figure 14: Environmental parameters.
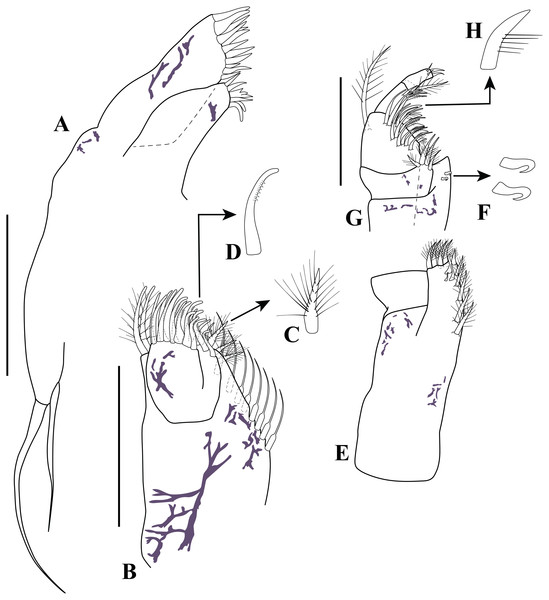
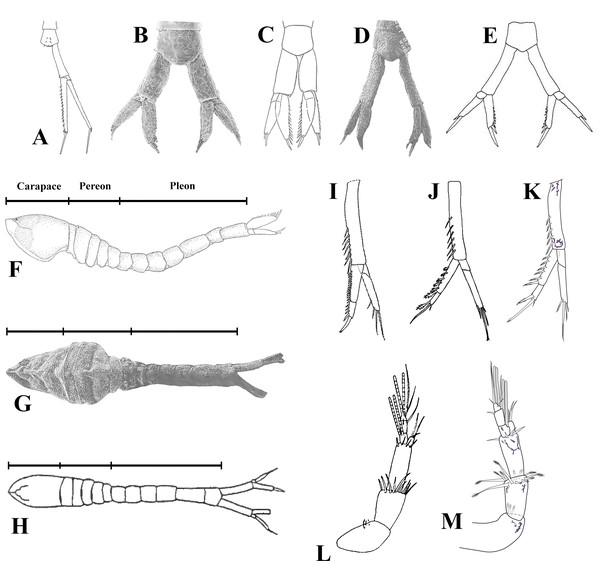
Mean values of environmental parameters measured at 24 stations per month in Maryland Coastal Bays during 2017–2019. Data are means ± SE. A, temperature; B, salinity; C, pH; D, DO.Figure 15: Illustrated key.
Uropods: (A) Pseudopicrocuma japonicum; (B) Picrocuma crudgingtoni; (C) P. poecilotum; (D) P. poecilotum; (E) P.rectangularis; (I) Spilocuma salomani; (J) Carinacuma watlingi comb. nov. K, C. umesi sp. nov. Male habitus: (F) Picrocuma poecilotum, lateral view; (G) P. poecilotum, dorsal view; (H) P. rectangularis, dorsal view. Antennules: (L) Carinacuma watlingi comb. nov.; (M) Carinacuma umesi sp. nov. Figures modified from: A Akiyama (2012); B, D, G, Tafe & Greenwood (1996); C, F, Hale (1945); E, H, Mühlenhardt-Siegel (2003); I, Watling (1977); J, L, Omholt & Heard (1979); K, M, Morales-Núñez and Chigbu (this study).Others peracarids co-occurring with the new species included: tanaidaceans (Tanaissus sp. Norman & Scott, 1906); amphipods (Acanthohaustorius intermedius Bousfield, 1965; Bathyporeia parkeri Bousfield, 1973; Parahaustorius longimerus Bousfield, 1965; P. wigleyi Bousfield, 1965); and cumaceans (Mancocuma cf. altera Zimmer, 1943 and Oxyurostylis smithi Calman, 1912).
| Stages | TBL (mm) | Carapace length (mm) | Pereon length (mm) |
Pleon length (mm) |
No. of micro-serrate seta with sub-terminal medial setule on inner margin of the uropodal peduncle | No. of serrate setae with single sub-terminal medial setule on inner margin of the uropodal endopod article 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-ovigerous female (with oöstegites) | ||||||
| 1 (Paratype, USNM: 1658951) | 2.3 | 0.56 | 0.61 | 1.11 | 1 | 6 |
| Ovigerous females | ||||||
| 1 (Holotype, USNM: 1658948) | 2.5 | 0.57 | 0.74 | 1.16 | 1 | 7 |
| 2 (Paratype, dissected, USNM: 1658949) | 2.3 | 0.59 | 0.69 | 1.06 | 1 | 6 |
| 3 (Paratype, USNM: 1658950) | 2.5 | 0.55 | 0.78 | 1.17 | 1 | 6 |
| Male | ||||||
| 1 (Paratype, USNM: 1658952) | 1.5 | 0.41 | 0.33 | 0.74 | 5 | 6 |
Remarks. The female of Carinacuma umesi sp. nov. specifically differs from that of its GoM congener C. watlingi by having: (1) maxilliped 3 carpus with inner margin having 4–5 simple setae (7–8 in C. watlingi), and (2) uropod peduncle with inner margin bearing one sub-distal micro-serrate seta with single sub-terminal medial setule (3–6 in C. watlingi).
Males of the new species can be differentiated from males of C. watlingi by: (1) antennule peduncle articles 1–2 sub-equal in length (article 2 shorter than article 3 in C. watlingi), (2) antennule accessory flagellum slightly longer than basal article of main flagellum (shorter in C. watlingi), (3) uropod peduncle 5.6 times as long as wide (6.5 in C. watlingi), and (4) uropod exopod article 1 twice as long as wide (1.4 times in C. watlingi).
Only two other vaunthompsoniine genera, Picrocuma Hale, 1936 and Pseudopicrocuma Akiyama, 2012 from southwest and northwest Pacific, respectively, have reduced thoracic exopods and males with clasping, geniculate antennae, and lack pleopods. In this respect they appear superficially similar to Carinacuma and Spilocuma. We consider, however, that the similarities of these geographically separated genera are unrelated and are due to homoplasy. One apparently important systematic character, which supports this view is the distantly different morphology of the uropods of the Atlantic genera, which have uniarticulated endopods, while those from the Pacific are biarticulated. Further, Carinacuma and Spilocuma have vestigial exopods on pereopod-4, which are absent on Picrocuma and Pseudopicrocuma. Although, these two unrelated Atlantic and Pacific taxa exhibit geniculate-clasping antennae, the specific morphological details of these appendages are distinctively different. The male of Carinacuma umesi sp. nov. is distinguished from those of the other vaunthompsoniine species, which lack pleopods, in the following identification key.
Key to the known males lacking pleopods within Vaunthompsoniinae
1. Antenna flagellum with five or six articles. Pereopod 4 without exopod. Uropod endopod uni-articulated (Figs. 5A–15E) …2
–Antenna flagellum with 10+ articles. Pereopod 4 having reduced or vestigial exopod. Uropod endopod bi-articulated (Figs. 15I–15K) …5
2. Antennule main flagellum composed of four articles. Uropod rami longer than peduncle (Fig. 15A) …Pseudopicrocuma japonicum (Akiyama, 2012)
–Antennule main flagellum composed of one or two articles. Uropod rami sub-equal to or shorter than peduncle length (Figs. 15B, 15D–15E) …3
3. Uropod peduncle broad, about twice as long as wide (Fig. 15B) …Picrocuma crudgingtoni Taft & Greenwood, 1996
–Uropod peduncle slender, at least three times as long as wide (Figs. 15D–15E) …4
4. Carapace length shorter than pereon length (Fig. 15G). Carapace-pereon length longer than pleon length (Fig. 15G) …Picrocuma poecilotum sensu (Tafe & Greenwood, 1996)
–Carapace length sub-equal to pereon length (Fig. 15H). Carapace-pereon length shorter than pleon length (Fig. 15H) …Picrocuma rectangularis Muhlenhardt-Siegel, 2003
5. Uropod endopod article 1 inner margin bearing 14 serrate setae (Fig. 15I). Uropod endopod article 2 inner margin bearing four serrate setae (Fig. 15I) …Spilocuma salomani Watling, 1967
–Uropod endopod article 1 inner margin bearing 5–6 serrate setae (Figs. 15J –15K). Uropod endopod article 2 inner margin bearing one serrate seta (Figs. 15J–15K) …6
6. Antennule: peduncle article 2 shorter than article 3 (Fig. 15L); accessory flagellum shorter than basal article of main flagellum (Fig. 15L) …Carinacuma watlingi (Omholt & Heard, 1979), comb. nov.
–Antennule: peduncle articles 2–3 sub-equal length (Fig. 15M); accessory flagellum slightly longer than basal article of main flagellum (Fig. 15M) …Carinacuma umesi sp. nov.
Hale (1936) created the monotypic genus Picrocuma, to receive the new species, P. poecilotum based on an ovigerous female holotype from Wynyard, Fossil Reef, Tasmania and in the same publication reported subadult specimens that he attributed to this species from Sellick’s beach Reef, Gulf St. Vincent’s Bay (South Australia). Later Hale (1945) described an adult male attributed to P. poecilotum based on a specimen from Table Bay, Tasmania, and reported a new northeastern range extension for this species to Myora Bight, Moreton Bay, Queensland. Besides its larger size and a geographical distance of over 1,600 km, there appear to be no major specific differences between the ovigerous female holotype of P. poecilotum and those examined by Tafe & Greenwood (1996) from Moreton Bay (see Tafe & Greenwood, 1996). Conversely, due to several morphological incongruencies between the original description of the male of P. poecilotum from Table Bay (Tasmania, (Hale, 1945)) and from Tangalooma (Moreton Bay, (Tafe & Greenwood, 1996)) such as: (1) the length of the carapace v s pereon length (longer in P. poecilotum from Tasmania (Fig. 15F) and shorter in P. poecilotum from Moreton Bay (Fig. 15G)), (2) the length of the carapace-pereon vs pleon length (shorter in P. poecilotum from Tasmania (Fig. 15F) and longer in P. poecilotum from Moreton Bay (Fig. 15G)), (3) the uropod shape (broadened in P. poecilotum from Tasmania (Fig. 15C) and slender in P. poecilotum from Moreton Bay (Fig. 15D)), and (4) the length of the uropod exopod vs uropod endopod length (shorter in P. poecilotum from Tasmania (Fig. 15C) and sub-equal in P. poecilotum from Moreton Bay (Fig. 15D)); which indicates that the male of P. poecilotum described by Hale (1945) from Table Bay (Tasmania) is not conspecific and appears to represent an undescribed species (Tafe & Greenwood, 1996). Until adult males attributed to P. poecilotum sensu Hale (1945) are examined and compared in detail, and, if feasible, a molecular study can be conducted to determine if P. poecilotum populations from both areas of Australia are conspecifics, the taxonomic status of this species remains unresolved. For these reasons, morphological features from the male of P. poecilotum (p. 473; fig. 68–F) presented by Tafe & Greenwood (1996) were used.
Discussion
During a previous study by Morales-Núñez & Chigbu (2016), Carinacuma umesi sp. nov. was misidentified as Spilocuma watlingi, in MCB. This record now represents the first confirmed occurrence of C. umesi on the East Coast of North America. With the description of C. umesi, three of the seven vaunthompsoniine species with males lacking pleopods now occur in the northwest Atlantic (Fig. 2).
According to Omholt & Heard (1979), Carinacuma watlingi occurs most commonly in shallow-water with sand substrata adjacent to low energy barrier island beaches. A similar situation was found for C. umesi collected from Maryland Coastal Bays and associated barrier-island systems. Therefore, it is likely that members of the genus Carinacuma are generally restricted to subtidal, shallow-water in fine sandy substrata along protected beaches adjacent to the inlets of coastal bays and estuaries.
The discovery of Carinacuma umesi is the result of a more intensive fine (0.5 mm) sieving screening effort and more careful examination of the smaller coastal marine invertebrates in MCBs. Further, the small size of C. umesi, in conjunction with lack of taxonomic expertise might have led to their being overlooked or misidentified in previous benthic studies of these mid-Atlantic coast bays by other investigators (Llansó, Scott & Kelley, 2002; Llansó, Scott & Kelley, 2003; Llansó, Scott & Kelley, 2004; Llansó, Scott & Kelley, 2005; Llansó, Scott & Kelley, 2006; Llansó & Dew, 2010; Llansó, 2015). For the same reason, it would not be surprising if the geographical range of C. umesi, currently known from the MCBs, extends southward along the coast of the South Atlantic Bight (SAB).
Conclusion
Carinacuma gen. nov., which is represented by two species, C. umesi and C. watlingi, is endemic to East and Gulf coasts of North America and appear to have no systematic affinities to the superficially similar western Pacific genera Picrocuma and Pseudopicrocuma. It has its closest systematic relationship with the North American genera Spilocuma and Mancocuma.
Heretofore the lack of published records for Carinacuma umesi from the East Coast of North America might have been due to the artifacts of sampling (e.g., sieve mesh-sizes too large to retain small species), and lack of taxonomic expertise to identify poorly known invertebrate taxa in the region.