PeerJ Section
Global Health
Welcome to your community’s home at PeerJ. Sections are community led and exemplify a research community’s shared values, norms and interests.
The citation average is 5.6 (view impact metrics).
27,339 Followers
Section Highlights
View all Global Health articles 
18 April 2024
Cytokine profiles of mild-to-moderate SARS-CoV-2 infected and recovered pre-vaccinated individuals residing in Indonesia
"The authors conducted original research regarding cytokine profiles among SARS-CoV-2 infected and recovered pre-vaccinated individuals in Indonesia with mild-to-moderate SARS-CoV-2 infection and those who recovered."
 Ramcés Falfán-Valencia, Handling Editor
Ramcés Falfán-Valencia, Handling Editor
 Ramcés Falfán-Valencia, Handling Editor
Ramcés Falfán-Valencia, Handling Editor
25 March 2024
Validation of the questionnaire “Pregnancy Vaccine Hesitancy Scale (pVHS)” toward COVID-19 vaccine for Malaysian pregnant women
"This article presents an important development in public health: the creation and validation of the pVHS-M, a specialized tool to measure COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy among pregnant women. This development is important for several reasons:
1) Urgency in Maternal Health: With the COVID-19 pandemic posing heightened risks for pregnant women, understanding vaccine hesitancy in this group is critical for maternal well-being.
2) Cultural Relevance: By tailoring the questionnaire to the Malay-speaking population, the study ensures accuracy and cultural appropriateness in assessing vaccine attitudes among Malaysian pregnant women.
3) Robust Validation: Through rigorous validation processes including content and face validation, as well as exploratory factor analysis, the pVHS-M emerges as a reliable and valid tool for assessing vaccine hesitancy attitudes and behaviors.
4) Targeting High-Risk Population: Focusing on pregnant women, especially those with high-risk pregnancies, allows for targeted interventions in a demographic particularly vulnerable to COVID-19.
This work intends thus to offer a precise instrument to understand and address COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy among pregnant women. Its development aims to facilitate tailored interventions and lays the groundwork for further research in diverse populations."
 Sonia Oliveira, Handling Editor
Sonia Oliveira, Handling Editor
 Sonia Oliveira, Handling Editor
Sonia Oliveira, Handling Editor

14 November 2023
Characteristic of persistent human papillomavirus infection in women worldwide: a meta–analysis
"Such a meta analysis is lacking in the HPV literature."
 Leny Jose, Handling Editor
Leny Jose, Handling Editor
 Leny Jose, Handling Editor
Leny Jose, Handling Editor
17 October 2023
The effect of drop-in centers on access to HIV testing, case finding, and condom use among female sex workers in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia
"This article is important as it assesses the impact of drop-in centers on access to HIV testing, case finding, and condom use among female sex workers in one specific setting. This information can be used to enhance similar settings or to adapt others."
 Carlos de Noronha, Handling Editor
Carlos de Noronha, Handling Editor
 Carlos de Noronha, Handling Editor
Carlos de Noronha, Handling Editor
4 September 2023
Assessing the impact of the 2018 tetanus guidelines on knowledge and practices of emergency physicians in trauma patients: a national survey study
"It is extremely important for healthcare professionals to be familiar with guidelines especially those dealing with emergencies, traumas or disasters to provide best care to the patient in a timely manner. This article sheds light on the awareness of guidelines among healthcare professionals in real world setting."
 Yusra Habib Khan, Handling Editor
Yusra Habib Khan, Handling Editor
 Yusra Habib Khan, Handling Editor
Yusra Habib Khan, Handling Editor
5 June 2023
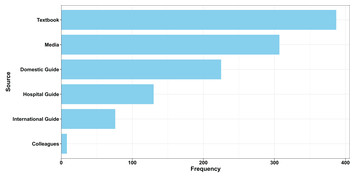
Determinants of acute undernutrition among pregnant women attending primary healthcare unit in Chinaksen District, Eastern Ethiopia: a case-control study
"This MS have significant impact to access undernutrition among Pregnant Women in specific reagion that may be used for managment of undernutrition in pregnant women."
 Mohammed Kuddus, Handling Editor
Mohammed Kuddus, Handling Editor
 Mohammed Kuddus, Handling Editor
Mohammed Kuddus, Handling Editor
15 May 2023
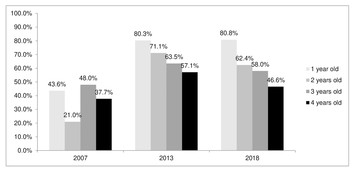
The effectiveness of hepatitis B vaccine in toddlers based on the five-year period national basic health research (Riskesdas 2007, 2013 and 2018) in Indonesia
"The study on the effectiveness of the hepatitis B vaccine in Indonesia and the need for a long-term evaluation of the immunization program is of significant public importance. Hepatitis B is a serious and potentially life-threatening disease that affects millions of people worldwide. In Indonesia, the disease is particularly prevalent, with an estimated 6-10% of the population being infected.
The study highlights the progress that has been made in reducing the prevalence of hepatitis B in children with complete vaccination, but also underscores the need for continued efforts to improve immunization coverage and program quality. The findings of the study could inform public health policy and interventions aimed at reducing the burden of hepatitis B in Indonesia.
By emphasizing the importance of ensuring that the initial dose of the vaccine is given within the first 24 hours of birth, monitoring nutritional status, and conducting genomic surveillance of HBV, the study provides valuable insights into the various factors that need to be considered in the design and implementation of an effective hepatitis B immunization program.
Overall, the study has important implications for public health in Indonesia and beyond, and highlights the need for ongoing efforts to prevent and control the spread of hepatitis B."
 Shailendra Verma, Handling Editor
Shailendra Verma, Handling Editor
 Shailendra Verma, Handling Editor
Shailendra Verma, Handling Editor
24 April 2023
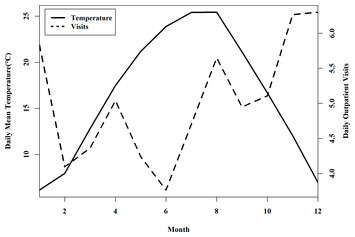
Effects of ambient temperature on atopic dermatitis and attributable health burden: a 6-year time-series study in Chengdu, China
"This article shows the effects of ambient temperature on atopic dermatitis and attributable health burden"
 Tian Li, Handling Editor
Tian Li, Handling Editor
 Tian Li, Handling Editor
Tian Li, Handling Editor

24 March 2023
Experience and coping strategies of bowel dysfunction in postoperative patients with rectal cancer: a systematic review of qualitative evidence
"The authors provided a systematic review to integrate the qualitative research on the experience of bowel dysfunction and coping strategies in postoperative patients with rectal cancer."
 Bruno Fionda, Handling Editor
Bruno Fionda, Handling Editor
 Bruno Fionda, Handling Editor
Bruno Fionda, Handling Editor

20 March 2023
Spatial heterogeneity in the exclusive use of hygienic materials during menstruation among women in urban India
"This study aimed to understand the spatial heterogeneity across Indian districts in the use of hygienic menstrual materials among young urban women, using data from the National Family Health Survey-5. The study found that 66.8% of urban women exclusively use hygienic materials, but there was considerable variation across districts. Positive spatial autocorrelation was identified, and cluster and outlier analysis revealed cold-spots in central Indian districts and hotspots in south Indian districts. The study identified women’s years of schooling, marital status, social group, and household wealth as major determinants of exclusive use of hygienic materials.
The study's findings suggest that there is a need for targeted and context-specific interventions and programs to improve menstrual hygiene practices among urban women in India. This could include interventions to increase education levels and household wealth, as well as programs that take into account the social and cultural factors that influence menstrual hygiene practices. The study also highlights the importance of understanding spatial heterogeneity when designing and implementing public health interventions. By identifying hotspots and cold-spots in menstrual hygiene practices, interventions can be tailored to the specific needs of different regions and populations. Overall, the study emphasizes the importance of addressing menstrual hygiene as a key aspect of women's health and dignity in India."
 Abhijit Pakhare, Handling Editor
Abhijit Pakhare, Handling Editor
 Abhijit Pakhare, Handling Editor
Abhijit Pakhare, Handling Editor
Collections
View all 
Relative Energy Deficiency in Sports (RED-S)

Artificial Intelligence for Mental Health: Advancements, Challenges, and Ethical Implications

PeerJ at 10 - our first 30 papers.

Advances in Illuminating the Druggable Genome
Food Safety Issues During- and Post-Pandemic/Epidemic Situations; Production, Packaging, Storage, and Analysis Interventions

27,339 Followers